Masih ingatkah teman-teman dengan kisah mukjizat Nabi Musa yang membelah laut merah dengan tongkatnya? Jika salah satu diantara teman-teman yang menganggap kisah tersebut hanya merupakan dongeng belaka, sekarang mari kita simak tulisan yang saya uraikan dibawah ini.
Seorang Arkeolog bernama Ron Wyatt pada ahir tahun 1988 silam mengklaim bahwa dirinya telah menemukan beberapa bangkai roda kereta tempur kuno didasar laut merah. Menurutnya, mungkin ini merupakan bangkai kereta tempur Pharaoh yang tenggelam dilautan tsb saat digunakan untuk mengejar Musa bersama para pengikutnya.
Menurut pengakuannya, selain menemukan beberapa bangkai roda kereta tempur berkuda, Wyatt bersama para krunya juga menemukan beberapa tulang manusia dan tulang kuda ditempat yang sama.
Temuan ini tentunya semakin memperkuat dugaan bahwa sisa2 tulang belulang itu merupakan bagian dari kerangka para bala tentara Pharaoh yang tenggelam di laut Merah. Apalagi dari hasil pengujian yang dilakukan di Stockhlom University terhadap beberapa sisa tulang belulang yang berhasil ditemukan,memang benar adanya bahwa struktur dan kandungan beberapa tulang telah berusia sekitar 3500 tahun silam, dimana menurut sejarah,kejadian pengejaran itu juga terjadi dalam kurun waktu yang sama.

poros roda dari salah satu kereta kuda
Selain itu, ada suatu benda menarik yang juga berhasil ditemukan, yaitu poros roda dari salah satu kereta kuda yang kini keseluruhannya telah tertutup oleh batu karang, sehingga untuk saat ini bentuk aslinya sangat sulit untuk dilihat secara jelas. Mungkin Allah sengaja melindungi benda ini untuk menunjukkan kepada kita semua bahwa mukjizat yang diturunkan kepada Nabi2-Nya merupakan suatu hal yang nyata dan bukan merupakan cerita karangan belaka. Diantara beberapa bangkai kereta tadi, ditemukan pula sebuah roda dengan 4 buah jeruji yang terbuat dari emas. Sepertinya, inilah sisa dari roda kereta kuda yang ditunggangi oleh Pharaoh sang raja.
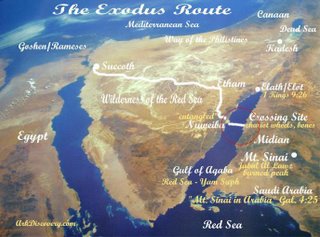
Sekarang mari kita perhatikan gambar diatas, Pada bagian peta yang dilingkari (lingkaran merah), menurut para ahli kira-kira disitulah lokasi dimana Nabi Musa bersama para kaumnya menyebrangi laut Merah. Lokasi penyeberangan diperkirakan berada di Teluk Aqaba di Nuweiba. Kedalaman maksimum perairan di sekitar lokasi penyeberangan adalah 800 meter di sisi ke arah Mesir dan 900 meter di sisi ke arah Arab. Sementara itu di sisi utara dan selatan lintasan penyeberangan (garis merah) kedalamannya mencapai 1500 meter. Kemiringan laut dari Nuweiba ke arah Teluk Aqaba sekitar 1/14 atau 4 derajat, sementara itu dari Teluk Nuweiba ke arah daratan Arab sekitar 1/10 atau 6 derajat
Diperkirakan jarak antara Nuweiba ke Arab sekitar 1800 meter.Lebar lintasan Laut Merah yang terbelah diperkirakan 900 meter. Dapatkah kita membayangkan berapa gaya yang diperlukan untuk dapat membelah air laut hingga memiliki lebar lintasan 900 meter dengan jarak 1800 meter pada kedalaman perairan yang rata2 mencapai ratusan meter untuk waktu yang cukup lama, mengingat pengikut Nabi Musa yang menurut sejarah berjumlah ribuan? (menurut tulisan lain diperkirakan jaraknya mencapai 7 km, dengan jumlah pengikut Nabi Musa sekitar 600.000 orang dan waktu yang ditempuh untuk menyeberang sekitar 4 jam).
Menurut sebuah perhitungan, diperkirakan diperlukan tekanan (gaya per satuan luas) sebesar 2.800.000 Newton/m2 atau setara dengan tekanan yang kita terima Jika menyelam di laut hingga kedalaman 280 meter. Jika kita kaitkan dengan kecepatan angin,menurut beberapa perhitungan, setidaknya diperlukan hembusan angin dengan kecepatan konstan 30 meter/detik (108 km/jam) sepanjang malam untuk dapat membelah dan mempertahankan belahan air laut tersebut dalam jangka waktu 4 jam!!! sungguh luar biasa, Allah Maha Besar.
Source :
http://misteridunia.wordpress.com/2008/10/26/mukjizat-nabi-musa/